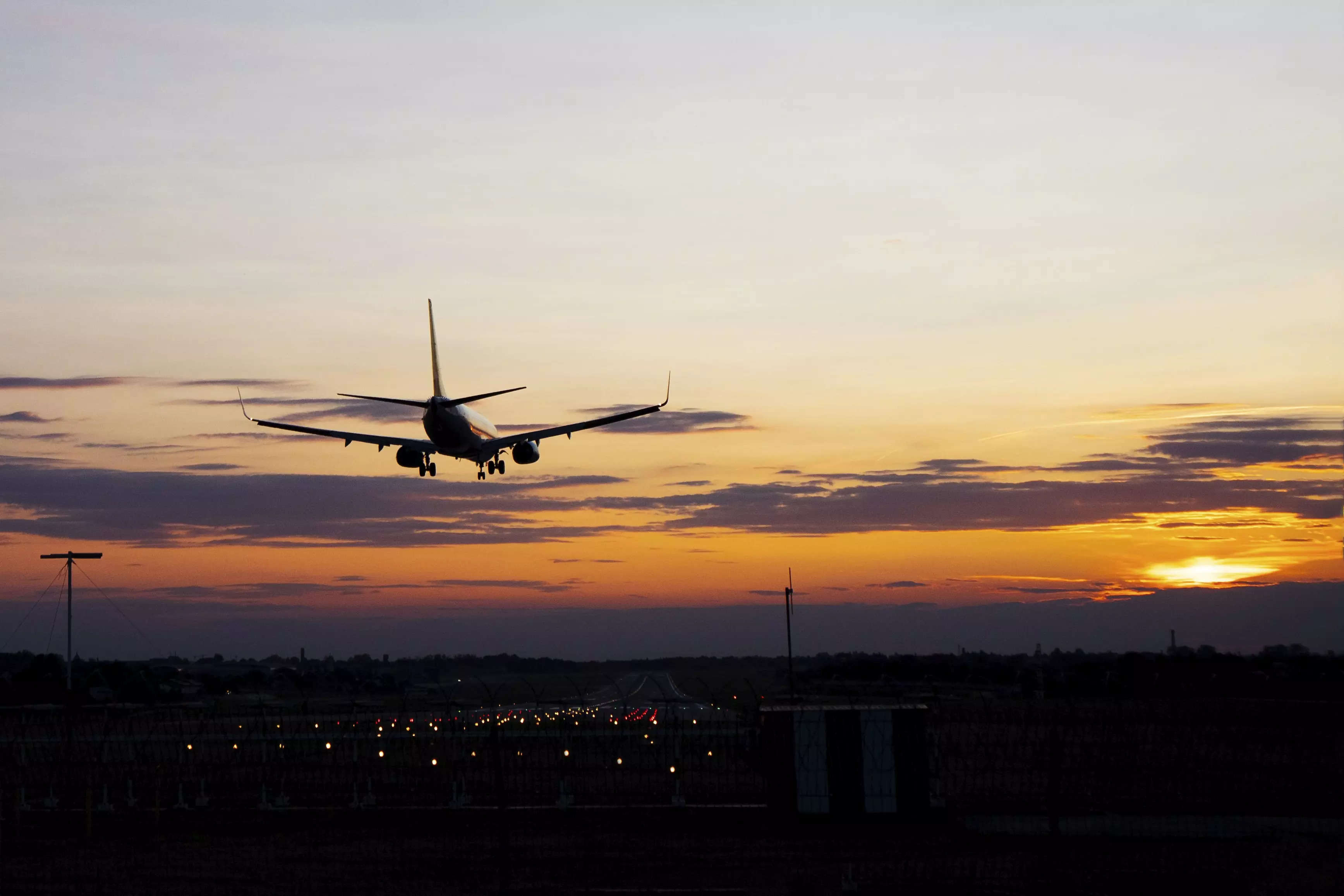
Climate change has made travelling by planes extra turbulent immediately than it was 4 a long time in the past, based on a examine.
The researchers from the University of Reading within the UK discovered that clear-air turbulence, which is invisible and unsafe to plane, has elevated in numerous areas all over the world.
The examine, revealed within the journal Geophysical Analysis Letters, discovered that at a typical level over the North Atlantic – one of many world’s busiest flight routes – the full annual length of extreme turbulence elevated by 55 per cent from 17.7 hours in 1979 to 27.4 hours in 2020.
Reasonable turbulence elevated by 37 per cent from 70.0 to 96.1 hours, and light-weight turbulence elevated by 17 per cent from 466.5 to 546.8 hours, the researchers stated. The staff famous that the will increase are per the results of local weather change. Hotter air from carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions is growing windshear within the jet streams, strengthening clear-air turbulence within the North Atlantic and globally.
“Turbulence makes flights bumpy and may often be harmful. Airways might want to begin fascinated by how they may handle the elevated turbulence, because it prices the business USD 150–500 million yearly within the US alone,” stated Mark Prosser, a PhD researcher on the College of Studying.
“Each further minute spent travelling by means of turbulence will increase wear-and-tear on the plane, in addition to the danger of accidents to passengers and flight attendants,” Prosser stated.Whereas the US and North Atlantic have skilled the most important will increase, the examine discovered that different busy flight routes over Europe, the Center East, and the South Atlantic additionally noticed important will increase in turbulence.
“Following a decade of analysis exhibiting that local weather change will enhance clear-air turbulence sooner or later, we now have proof suggesting that the rise has already begun,” stated Professor Paul Williams, an atmospheric scientist on the College of Studying who co-authored the examine.
“We ought to be investing in improved turbulence forecasting and detection techniques, to stop the rougher air from translating into bumpier flights within the coming a long time,” Williams added.